What Is the Definition of ‘Bearing’ in GPS Navigation?
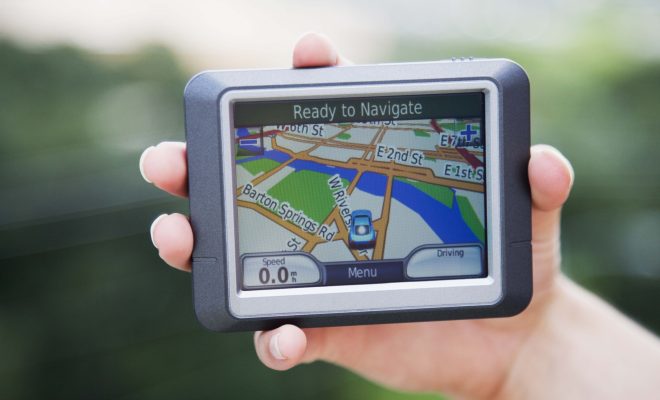

In GPS navigation, bearing is a term used to refer to the direction from your current location to a specific destination. This term is often used interchangeably with the term heading, but it should be noted that the two are not exactly the same.
Heading refers to the direction in which you are moving in real-time, while bearing refers to the direction in which you need to move to reach a destination from your current location. This means that even if you are not currently moving, you can still determine the bearing to a desired location.
Bearings are typically given in degrees, with 0 degrees representing true north, 90 degrees representing east, 180 degrees representing south, and 270 degrees representing west. Intermediate bearings can also be given, such as 45 degrees representing northeast and 135 degrees representing southeast.
In GPS navigation, determining your bearing to a specific location is important because it allows you to plan your route and navigate towards your destination. Many GPS devices and apps will display your current location and the bearing to your destination, making it easy to follow and adjust your path as necessary.
It should be noted that bearings are not always precise, and can be affected by factors such as terrain, atmospheric conditions, and interference from other devices. Additionally, since GPS relies on satellite signals, it may not always be accurate in areas with a lot of tall buildings or other obstructions.
Overall, bearing is an important concept to understand in GPS navigation, as it allows you to accurately navigate towards a specific location and plan your route accordingly.