What Is a Jumper?
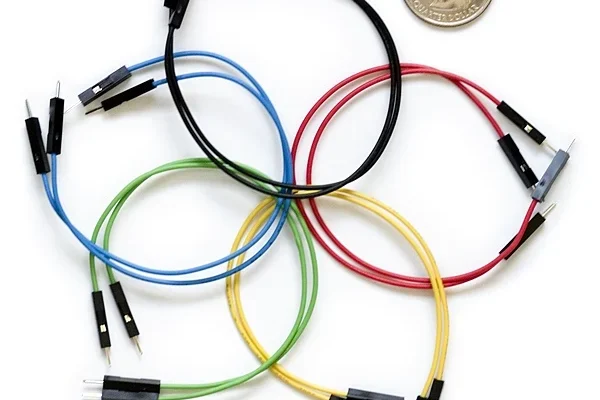

A jumper can refer to a piece of clothing or an electronic component, but in this article, we will focus on the latter.
In electronics, a jumper is a small device that is used to connect two points on a printed circuit board (PCB). Jumpers are usually made of metal and come in two types: shunt and open.
A shunt jumper is a small, metal piece that connects two electrical contacts on a circuit board. It works by closing the connection between the two contacts, allowing current to flow through them. Shunt jumpers are typically used to configure or modify the behavior of a circuit, such as selecting a different range of resistors or setting a different voltage threshold.
On the other hand, an open jumper is used to break the connection between two contacts. This is often used when testing a circuit or isolating a specific component from the rest of the circuit. An open jumper can also be used as a backup for a shunt jumper in case the connection needs to be broken temporarily.
Jumpers are usually found on older or simpler circuit boards, as modern PCBs often have surface-mounted components that do not require jumpers. However, jumpers are still commonly used in breadboarding and prototyping to quickly modify circuit behavior or isolate components.
Overall, jumpers are a simple but essential component in electronics. Without jumpers, it would be difficult to modify circuits or test individual components, making debugging and development much more challenging.