WAN technologies and services
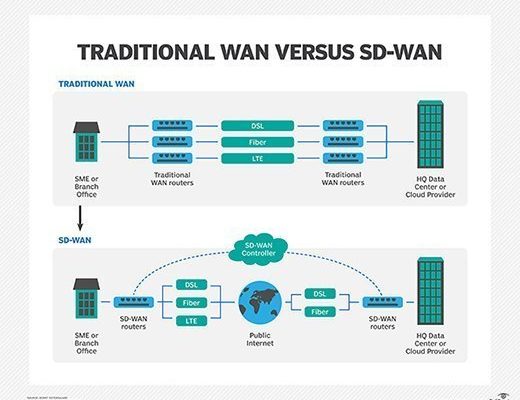
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a computer network that extends over a large geographic area such as a state, country, or even the entire globe. WAN technologies and services are used for connecting multiple local area networks (LANs) and devices over a long distance, enabling businesses and individuals to communicate and transfer data effortlessly.
In this article, we will explore some of the most commonly used WAN technologies and services, including their characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages.
1. Leased Lines
Leased lines are point-to-point connections between two locations that are provided by a telecommunication company, offering high-speed connectivity (up to 10Gbps). Such connections are often used by businesses that require a constant, reliable, and dedicated internet connection, such as large enterprises, government organizations, and financial institutions.
Advantages:
– Guaranteed bandwidth with symmetric download and upload speeds
– Always-on connection without any interruptions
– High level of security as leased lines are not shared with other users
Disadvantages:
– High cost due to the need for dedicated lines
– Long installation times, which can take several weeks or even months
– Limited scalability since additional lines are required to increase bandwidth.
2. MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching)
MPLS is a type of routing protocol that prioritizes traffic based on its labels rather than its IP addresses, reducing network congestion and improving the overall network performance. MPLS service providers offer VPN (Virtual Private Network) services that enable businesses to have multiple locations securely connected to their corporate networks over an MPLS backbone.
Advantages:
– High level of security as traffic is isolated and encrypted
– Consistent network performance with guaranteed bandwidth and low latency
– Flexible architecture that can easily scale to meet business needs
Disadvantages:
– High costs compared to other WAN technologies
– Limited feature set compared to other WAN technologies
– Limited scalability due to the need to upgrade the entire MPLS network infrastructure.
3. VPN (Virtual Private Network)
A VPN is a secure and encrypted tunnel created between two endpoints over a public or private network, providing users with a secure and private connection over an unsecured network such as the internet. VPNs are commonly used by remote workers, telecommuters, and businesses that require secure connections between their offices and employees.
Advantages:
– Low cost compared to other WAN technologies
– Easy to deploy and manage, making it ideal for small businesses and individuals
– High level of security, privacy, and encryption for data transmissions
Disadvantages:
– Limited bandwidth and network performance compared to other WAN technologies
– Performance degradation due to high network traffic
– Limited scalability beyond a certain number of VPN connections.
Final Thoughts:
WAN technologies and services provide vital connectivity, enabling businesses and individuals to communicate, transfer data, and access cloud-based services. While each WAN technology has its own characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages, selecting the right one depends on the needs of the business or individual. With the proper WAN technology selection and implementation, organizations can improve their network performance, reduce costs, and increase productivity.