How Does the KERS System in F1 Cars Work?
Formula One racing is an unparalleled display of speed, power, and technology. Although the design of the cars can vary considerably, the sport is constantly evolving to maintain a level playing field that challenges the drivers and their teams to push the boundaries of engineering. One of the most prominent technologies in F1 cars today is the Kinetic Energy Recovery System (KERS). This system has been in use since 2009 and has revolutionized the sport.
The KERS system works by converting the kinetic energy generated by the brakes into electrical energy that can be stored and reused later. When a driver brakes, the KERS system captures some of the energy generated and stores it in a battery pack. This energy can then be used to provide a boost of speed for a few seconds during acceleration.
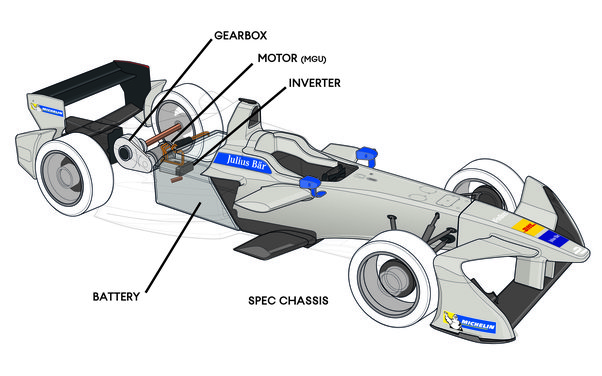
Essentially, the KERS system consists of three primary components that work together to achieve this goal:
1) Energy-Harvesting Unit: The first component is the energy-harvesting unit, which is located in the rear of the car. This unit captures the kinetic energy generated by the brakes and converts it into electrical energy.
2) Battery Pack: The second component is the battery pack, which is usually located inside the car’s chassis. This pack stores the electrical energy generated by the energy-harvesting unit and can release it later to boost acceleration.
3) Power Delivery System: The third component is the power delivery system, which controls the release of the electrical energy stored in the battery pack. The power delivery system works by sending the electrical energy to the car’s engine, which can use it to provide an extra boost of power.
The KERS system has revolutionized F1 racing, as it allows drivers to store energy generated during braking and then use it later to gain more speed. With the KERS system, drivers can now make up valuable ground and overtake other drivers during the race.
However, using the KERS system requires careful management. The battery has only been designed to hold a limited amount of energy, and once the energy is depleted, it can take time to recharge. This means that drivers are encouraged to use the KERS system cautiously, to ensure they have enough energy to last the race’s duration.
In conclusion, the KERS system in F1 cars has revolutionized the sport and provided a new level of excitement for drivers and spectators alike. The system enables drivers to maximize the energy generated during braking and to reuse it as a source of power during acceleration. With the KERS system, drivers need to optimize the use of the stored energy and rely on their instincts, judgement, and skill to get the most out of the race.





