DNS Servers: What Are They and Why Are They Used?
As an AI language model, I don’t have personal opinions but here’s the article you’re requesting for.
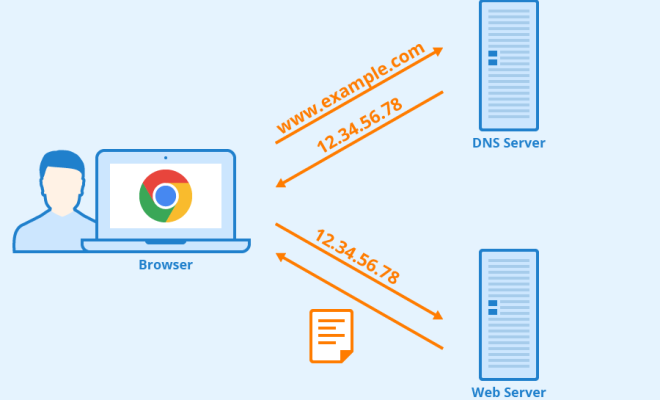
The domain name system (DNS) is one of the fundamental components of the internet. It enables us to access websites and other online services by translating domain names (e.g., mywebsite.com) into their corresponding IP addresses that computers understand. DNS servers, therefore, are crucial elements of this system, responsible for handling such translations and ensuring that traffic flows smoothly across the internet.
To understand the importance of DNS servers, let’s delve a little deeper into how the DNS system works. When we enter a domain name into our computer or smartphone’s web browser, it sends a request to a nearby DNS resolver (often the one provided by an internet service provider or ISP). The resolver performs a broad search across the internet, starting from the top-level domain servers (such as .com, .org, etc.) and working its way down the hierarchy, until it finds the IP address associated with the requested domain name.
If the resolver doesn’t have information about the requested domain name, it sends a request to the authoritative DNS server for that domain. The authoritative server is responsible for providing the IP address or other relevant information about the requested domain name. The resolver then caches the results, so it can respond more quickly if the same domain name is requested again in the future.
There are several reasons why DNS servers are so important. Firstly, they play a critical role in ensuring the reliability and redundancy of the internet. The DNS system is designed to be distributed, with thousands of DNS servers worldwide. This means that if one server fails, other servers can still handle requests, preventing downtime and ensuring that users can access websites and services without interruption.
Secondly, DNS servers play a vital role in internet security. They can help prevent phishing attacks, malware infections, and other types of cyber threats by blocking access to known malicious websites or warning users about potential risks. By detecting and blocking malicious domains or IP addresses, DNS servers help keep the internet a safer place for everyone.
Lastly, DNS servers are essential for managing and maintaining web applications and services. For example, website owners can use DNS servers to redirect traffic to different domains or servers, manage email servers or subdomains, and track web traffic and other analytics. Without DNS servers, it would be much harder to manage the complex web infrastructure that powers the internet today.
In conclusion, DNS servers are a critical component of the internet’s infrastructure, responsible for translating domain names into IP addresses and managing web traffic across the internet. They play a vital role in ensuring the reliability, security, and performance of the internet, and without them, the web as we know it today would not exist.