What is Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)?
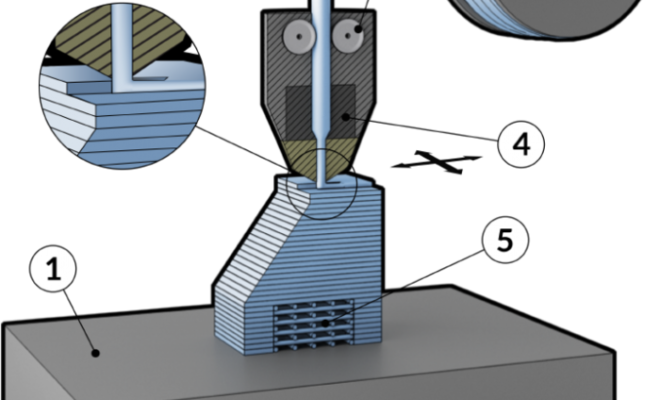
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is a technology used in the field of additive manufacturing or 3D printing, and it is one of the most commonly used techniques in the industry today. It is also known as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) and is widely used for prototyping, tooling, and creating production parts for various industries.
The basic principle behind FDM is simple – melted plastic is extruded through a small nozzle and carefully layered to create a three-dimensional object. The plastic material is fed into the printer in a filament form, and it is then heated and melted inside the printer’s extruder, which is a small chamber where the molten plastic is formed into a thin filament. The filament is then extruded through the printer’s nozzle and deposited layer by layer onto a build platform or a previously printed layer to create the final 3D object.
FDM printers are versatile and can use a variety of different materials, including ABS (Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene), PLA (Polylactic acid), and PETG (Polyethylene terephthalate glycol). Additionally, some printers can print with specialty materials like flexible filaments, fire-retardant materials, and even some metals.
FDM is known for its speed and accuracy, as it can produce parts quickly and efficiently. The process is also cost-effective, making it ideal for small batch production or creating customized parts to replace obsolete or hard-to-find components.
One of the most significant advantages of FDM is its ease of use. Many printers can be easily controlled through a user-friendly interface and can accept 3D models generated from a wide array of CAD software programs. Once the 3D model is loaded, the printer can start the build process, and the operator can perform other tasks while the printer works in the background. This makes it ideal for small businesses, hobbyists, or individuals who want to create a 3D object but do not have extensive training or engineering knowledge.
FDM has its limitations, however, and may not be suitable for all types of 3D printing applications. For example, FDM may not produce as detailed surfaces as other techniques, and the printed parts may not be as strong or sturdy as parts produced through injection molding or other types of manufacturing processes.
In conclusion, Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is an important 3D printing technology that has revolutionized the manufacturing industry. It is a fast, cost-effective, and user-friendly method for creating 3D objects in small quantities or for prototyping. While it may not be suitable for all applications, it has certainly established itself as a leading technology in the field of additive manufacturing.






