PLA vs. ABS Filaments for 3D Printing: What’s the DIfference?
3D printing has been making waves in the manufacturing and prototyping industry, with its ability to print complex shapes and structures with high accuracy. The two most commonly used filaments in 3D printing are PLA and ABS.
While both filaments have their own advantages, understanding their differences can help in deciding which one to use for a particular project.
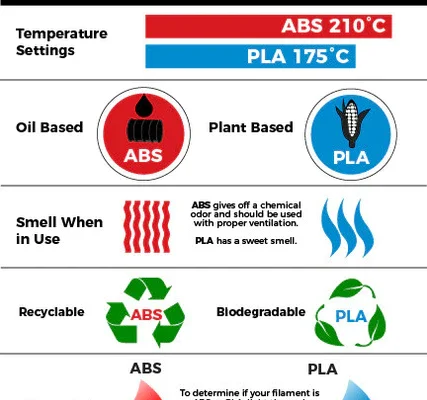
PLA, or Polylactic Acid, is a biodegradable and easy to use filament. It has a lower printing temperature and produces less warping and cracking than ABS. This makes it ideal for printing objects with higher details or intricate shapes. PLA is made from renewable sources such as cornstarch, sugarcane, and cassava, making it eco-friendly and sustainable. Its wide range of colors and finishes, including matte, glossy, and transparent, make it popular for decorative 3D prints.
ABS, or Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, is a durable and robust filament that can withstand high temperatures. This makes it suitable for printing functional parts that require strength, such as gears, machine parts, and toys. ABS has a higher printing temperature and is prone to warping, which means it requires a heated bed and enclosed space for optimal printing. Its wide range of colors, including opaque and glossy finishes, make it popular for functional 3D prints.
While PLA is considered a more eco-friendly and easier to print filament than ABS, it is not as strong and durable.
PLA objects can become brittle over time when exposed to sunlight or high temperatures. ABS, on the other hand, can withstand higher temperatures and is less prone to breakage. However, ABS is more difficult to print and requires a higher level of expertise and equipment, making it a less popular choice for beginners.
In conclusion, choosing between PLA and ABS for 3D printing depends on the intended use and requirements of the object. PLA is best suited for decorative objects and those with intricate shapes, while ABS is preferred for functional parts that require strength and can withstand higher temperatures. Both filaments have their own advantages and disadvantages, and it is important to consider these factors before deciding which one to use for a particular project.






