How to Use a Bladder Scanner: 8 Steps
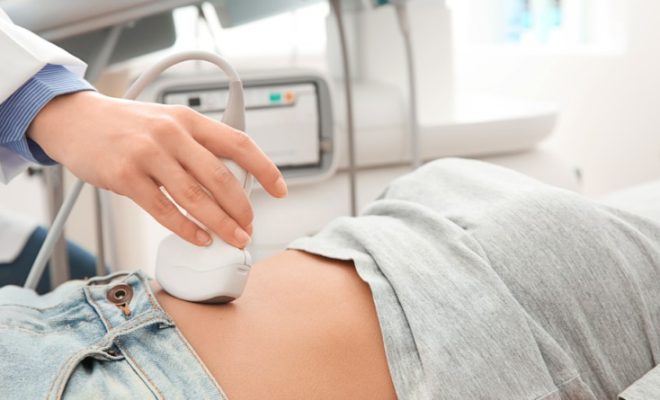

Introduction:
A bladder scanner is a non-invasive, portable ultrasound device that measures the volume of urine in the bladder. It is widely used by healthcare professionals to assess patients with urinary retention or incontinence issues, as well as monitor postoperative patients. Here are 8 essential steps for using a bladder scanner correctly.
Step 1: Prepare the patient
First, inform the patient about the procedure and its purpose if they are alert and oriented. Ensure that they are lying comfortably in a supine position. Ask the patient to remain still during the scanning process to ensure accurate results.
Step 2: Position the patient
It is important to have the patient’s legs extended and slightly apart to provide good visibility of the pelvic area. Place a folded towel under their lower back to slightly elevate it and promote a more favorable angle for scanning.
Step 3: Apply gel
Before pressing the scanner probe against the skin, apply a generous amount of ultrasound gel on the probe’s surface. This ensures better contact and improves sound wave transmission through tissues.
Step 4: Locate the bladder
Hold the bladder scanner probe gently but firmly against the patient’s lower abdomen. Begin searching for bladder landmarks such as bilateral iliac arteries or internal iliac veins by following on-screen guidelines provided by your scanner.
Step 5: Obtain an image
Once you have located the bladder, adjust your angle until you obtain an optimal image on your scanner screen that covers all the contours of the bladder. Make sure that there is minimal bowel gas, which can obstruct clear images, before proceeding.
Step 6: Measure urine volume
Activate your scanner’s automatic volume measurement feature once you have achieved a satisfactory image. The device will calculate urine volume within seconds and display relevant values on its screen.
Step 7: Record data
Document bladder volume measurements in your patient’s medical record, including time and date. You might also note down the patient’s position and any challenges during the scanning process, such as excess gas in the bowel or large scars that might disrupt ultrasound efficiency.
Step 8: Clean up
Remove remaining ultrasound gel from the probe and patient’s skin. Disinfect the probe according to your facility’s protocol. Store the bladder scanner after cleaning as directed by your facility guidelines.
Conclusion:
A bladder scanner is a vital tool for healthcare professionals that provides quick and accurate systematic measurements of urine volume. By following these eight simple steps, you can effectively perform a bladder scan, monitor patient conditions, and help plan appropriate interventions accordingly.