How to Push a Hernia Back in: 15 Steps
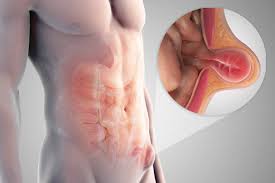
A hernia occurs when an internal organ or tissue protrudes through a weak area in the surrounding muscle or tissue. It can cause discomfort and pain, and in some cases, it may require urgent medical attention. If you suspect you have a hernia and want to attempt to push it back in temporarily before seeking medical help, follow these 15 steps carefully.
1.Make sure the area around the hernia is clean: Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before attempting to touch the affected area.
2.Lie down on a flat surface: Find a comfortable position where your body is relaxed and the pressure on your hernia is reduced.
3.Examine the bulge: Gently feel the bulge to determine its size, shape, and consistency.
4.Apply a cold compress: Place a cold compress on the affected area for a few minutes to reduce swelling and inflammation.
5.Use over-the-counter pain relievers if needed: Take appropriate over-the-counter pain medications to help alleviate discomfort during this process.
6.Relax your muscles: Take slow, deep breaths to help relax your muscles around the herniated area.
7.Apply gentle pressure: Using your fingertips, gently press on the edges of the bulge while maintaining steady pressure.
8.Push the bulge inward: Gradually apply more pressure, pushing the hernia back into its original location within your body cavity.
9.Hold it in place: Once you’ve successfully pushed the hernia back in, hold it in place with your hand for several minutes to prevent it from slipping out again.
10.Wear supportive garments: Use an abdominal binder or hernia belt for added support and to help keep the organ in place.
11.Avoid heavy lifting and straining: Refrain from activities that may exert excessive strain on your abdominal muscles – such as heavy lifting or intense exercise.
12.Use proper lifting techniques: If you must lift objects, follow proper lifting techniques, such as using your legs instead of your back and bending at your knees.
13.Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can place additional pressure on your abdomen, increasing the risk of hernia recurrence.
14.Speak to a doctor: Consult a medical professional for advice on managing your hernia and to discuss potential treatment options.
15.Keep an eye on symptoms: Observe any changes in the condition of your hernia, and seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe pain, fever, or vomiting.
Remember, pushing a hernia back in is only a temporary solution, and should not be considered a permanent fix. It’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for appropriate diagnosis and treatment of a hernia.