How to calculate p e ratio

In the world of investing, there are countless terms and concepts that investors must become familiar with. One of the most important and widely-used valuation metrics is the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio. This ratio is an essential tool to help investors quickly gauge a stock’s value relative to its earnings. In this article, we will delve into what this ratio is, how it’s calculated, its significance, and some caveats you should keep in mind.
What is the P/E Ratio?
The price-to-earnings ratio is a valuation metric that investors use to compare the market price of a stock against its earnings per share (EPS). In essence, it indicates how much an investor is willing to pay for every dollar of earnings generated by the company.
Calculating the P/E Ratio
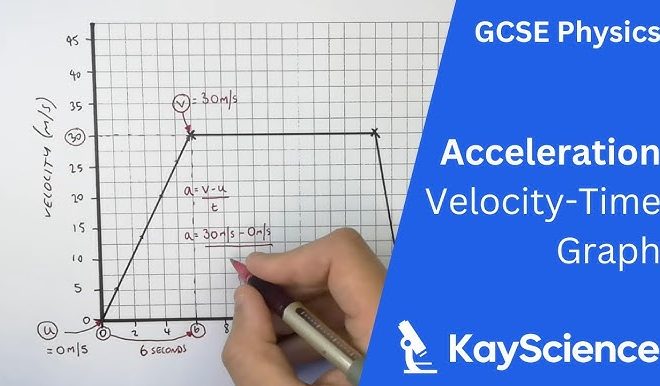
To calculate the P/E ratio, you’ll need two main components: the stock’s current market price and its earnings per share. Here’s the formula for calculating the P/E ratio:
P/E Ratio = Stock Price / Earnings per Share (EPS)
1. Stock Price: The current market price of a single share of the stock, which you can find on any financial platform or your broker’s website.
2. Earnings per Share (EPS): EPS represents a company’s total earnings divided by its outstanding shares. It is usually stated in financial statements and annual reports or available through financial websites.
Now that you have both components, simply divide the current stock price by the EPS to determine the P/E ratio.
Example:
Let’s assume Company X has a current stock price of $50 and an EPS of $5.
P/E Ratio = $50 / $5 = 10
In this instance, Company X has a P/E ratio of 10. This means that investors are willing to pay $10 for every $1 of earnings generated by Company X.
Significance of the P/E Ratio
The P/E ratio holds great value for investors as it enables them to quickly determine the relative value of stocks.
Here are some of its key uses:
1. Comparing stocks: By comparing the P/E ratios of different companies within the same industry, investors can identify which stocks are overvalued or undervalued. It is important to remember that this comparison should be made among firms in the same industry, as P/E ratios can vary greatly between different sectors.
2. Assessing growth prospects: A high P/E ratio can indicate that investors expect a company to have higher growth rates in the future, whereas a low P/E ratio may indicate slower growth or that the stock is undervalued.
Caveats When Using the P/E Ratio
As useful as the P/E ratio is for making investment decisions, there are some limitations you should be aware of:
1. It’s not suitable for comparing companies in different industries, as each industry has unique characteristics that influence their valuation metrics.
2. The ratio relies on accounting earnings, which can be manipulated and may not always reflect the true financial performance of a company.
3. It does not account for differences in risk among companies and should be used together with other valuation metrics.
In conclusion, while the price-to-earnings ratio serves as a valuable tool for investors to gauge a stock’s value relative to earnings, it’s essential to keep its limitations in mind and use it in conjunction with other valuation methods. By doing so, you’ll be well-equipped to make informed investment decisions.