How to calculate moisture content
Introduction
Moisture content is an essential factor in various industries, such as agriculture, construction, and food processing. It determines the amount of water present in a substance, which can significantly impact the product’s quality, shelf life, and overall performance. In general, moisture levels can be determined using different techniques and tools that cater to the unique requirements of each industry. This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to calculate moisture content for various applications.
Methods to Calculate Moisture Content
1. Gravimetric Method:
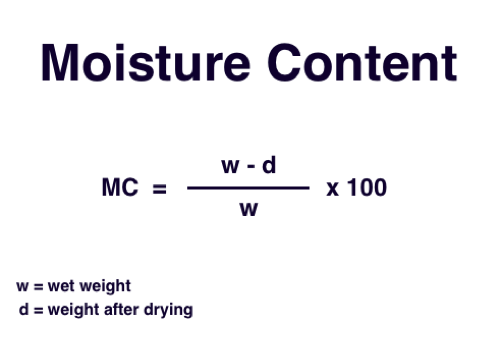
The gravimetric method, also known as the oven-drying method, is one of the most accurate and straightforward techniques for calculating moisture content. It involves weighing the sample before drying and after drying. The difference in mass (weight loss) is considered as the moisture content. To calculate the percentage of moisture content, follow these steps:
a) Weigh the wet or moist sample (W1).
b) Dry the sample in an oven at a temperature suited for that specific material.
c) Weigh the dry sample once it has reached a constant weight (W2).
d) Calculate the moisture content percentage using this formula:
Moisture Content (%) = [(W1 – W2) / W1] x 100
2. Loss on Drying (LOD) Method:
The loss on drying method measures moisture content based on weight loss during heating or drying using a specialized tool called Moisture Balance Analyzer. The process is fast and non-destructive.
a) Place a moist sample into a specialized moisture balance analyzer.
b) The instrument measures and records initial weight of the sample.
c) The analyzer heats or dries the sample until reaching a constant weight.
d) The instrument calculates and displays percentage moisture content based on initial weight and final dry weight.
3. Karl Fischer Titration Method:
Karl Fischer titration is a highly accurate and selective method used specifically for determining water content in various substances. It uses titration, a reagent called Karl Fischer reagent (containing iodine), and an electrochemical sensor to detect the endpoint of the titration.
a) Prepare a sample by dissolving it in an appropriate solvent.
b) Introduce the sample into the titration vessel containing Karl Fischer reagent.
c) The instrument measures the added reagent volume required to reach the endpoint.
d) Calculate moisture content as a percentage by relating reagent volume to sample’s weight.
4. Near-Infrared (NIR) Spectroscopy Method:
This non-destructive method utilizes near-infrared light reflection from samples to determine moisture content based on characteristic absorption bands of water molecules.
a) Obtain a calibrated NIR spectrophotometer instrument.
b) Place the moist sample into the instrument.
c) The instrument detects moisture content based on reflected light intensity and wavelength.
d) Use predetermined calibration curves to convert light absorption values into moisture percentages.
Conclusion
Several methods are available for determining moisture content in materials, catering to their unique characteristics and requirements. Common methods include gravimetric, loss on drying (LOD), Karl Fischer titration, and near-infrared spectroscopy techniques. In choosing the appropriate technique, consider factors such as accuracy, sensitivity, time consumption, cost, and material type. By selecting the most suitable method, you can maintain product quality and compliance with industry standards while optimizing production processes.






