A glossary for the terms and types of WAN technologies
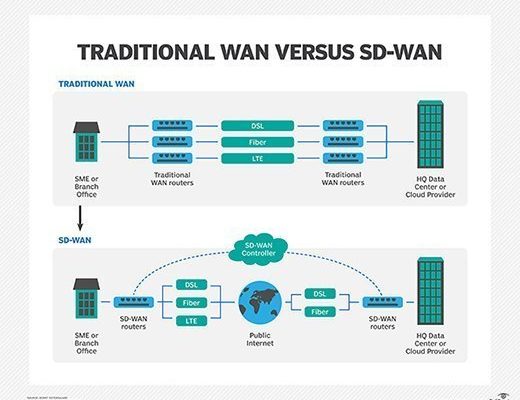
Wide Area Networks (WAN) are essential in today’s global and highly connected world. They are used to connect networks across geographical distances and enable access to resources and applications. Many technologies form the backbone of these networks, and understanding these technologies is crucial to designing, implementing, and managing WANs effectively. In this article, we provide a glossary of common terms and types of WAN technologies.
1. Circuit Switching: It is a technology that connects two devices with a dedicated physical line to transmit data. The line remains reserved for the devices until the transmission is complete, making the system less flexible than packet switching.
2. Packet Switching: Unlike circuit switching, packet switching divides data into small packets to be transmitted over a shared network. These packets are then reassembled at the destination. Packet switching optimizes bandwidth utilization and allows multiple conversations over a single network.
3. Frame Relay: A WAN technology that uses packet switching to transmit data over leased lines, Frame Relay divides data into fixed-size packets called frames. At the receiving end, these packets are reassembled to create the original data.
4. Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM): A WAN technology that uses a cell-switching approach, it divides data into small cells, which are transmitted across the network. ATM optimizes bandwidth usage by employing pre-assigned virtual circuits, which guarantee bandwidth allocation for each connection.
5. Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS): A popular WAN technology, MPLS uses label switching to route packets over the network. It employs a combination of circuit and packet switching to guarantee Quality of Service (QoS) – an essential requirement for real-time applications.
6. Metro Ethernet: A WAN technology that uses Ethernet to connect LANs across a metropolitan area. It boasts high bandwidth, low latency, and is cost-effective compared to other WAN technologies.
7. Virtual Private Network (VPN): A VPN is a secure tunnel that enables remote users to access a private network over a public network like the Internet. VPNs are widely used for remote connectivity and secure data transmission.
8. Dedicated leased lines: Traditional WAN technology that connects devices directly with dedicated physical lines. Leased lines provide a guaranteed quality of service and high availability, but are expensive compared to other technologies.
9. Wireless WAN: A WAN technology that uses different wireless technologies like Wi-Fi, Cellular networks, and satellite communication to connect networks across vast distances. It is ideal for remote locations where installing physical cables is challenging.
In conclusion, WAN technologies have evolved, and there are currently many options in the market. Understanding the differences between these technologies is essential in choosing the best fit for your organization. The above glossary provides you with relevant terms and types to start and guide you in your research.