3 Ways to Treat Lipedema
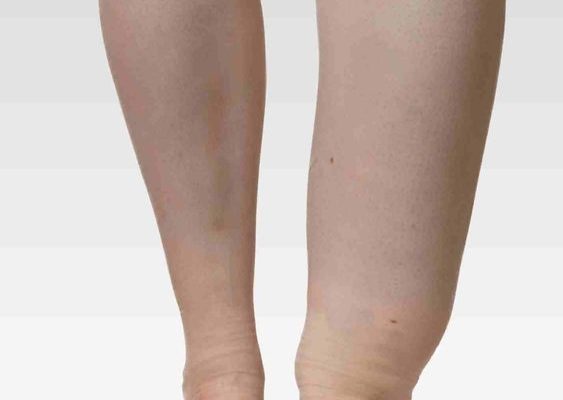
Lipedema is a chronic, progressive condition characterized by an abnormal accumulation of fat cells in the legs, and sometimes the arms. The disorder predominantly affects women and can lead to both physical and emotional discomfort. Although there is no known cure for lipedema, there are various treatment options available to help manage the symptoms, reduce pain, and improve overall quality of life. In this article, we will explore three ways to treat lipedema effectively.
1. Compression Therapy
Wearing compression garments can help alleviate some of the discomfort caused by lipedema. Graduated compression stockings, made with strong elastic fabrics, encourage blood flow from the lower extremities back towards the heart. This helps to reduce swelling, minimize heaviness in the limbs, and prevent fluid build-up.
Pneumatic compression devices are another method of providing compression therapy. These devices consist of a pump that inflates and deflates sleeves or cuffs wrapped around the affected limbs. The pressure generated by pumping air into the cuffs can help reduce fluid build-up and lymphatic congestion.
If you decide to incorporate compression therapy into your treatment plan, consult a certified lymphedema therapist or medical professional regarding appropriate garment size and pressure strength.
2. Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD)
Manual lymphatic drainage is a specialized type of massage designed to stimulate the lymphatic system and redirect accumulated lymphatic fluid away from swollen regions towards healthier pathways. This technique is commonly recommended for managing symptoms related to lipedema.
A trained therapist usually performs MLD by applying light pressure with slow, rhythmic strokes following specific pathways. It is essential to visit an experienced therapist familiar with treating lipedema patients for optimal results.
Patients can also learn self-MLD techniques for ongoing maintenance between therapy sessions under a therapist’s guidance. However, manual lymphatic drainage may not be suitable for people with certain health conditions like active cancer, deep vein thrombosis, or congestive heart failure.
3. Surgical Interventions
For patients with advanced lipedema or those who have not responded well to conservative treatments like compression and MLD, surgical treatment options may be considered. These interventions may vary depending on the severity of lipedema and individual patient needs. Some common surgical procedures include:
– Liposuction: This procedure targets fat deposits beneath the skin and helps contour the affected limbs. Water-assisted or tumescent liposuction techniques are recommended for lipedema patients to minimize trauma to the nearby lymphatic vessels.
– Lymphatic Sparing Tissue Excision: This surgery removes excess skin and fatty tissue while preserving the lymphatic structures. It is generally performed for patients with loose skin and severe lipedema stages.
Remember to consult a healthcare professional experienced in treating lipedema before committing to a surgical intervention. Discuss your condition, symptoms, and expectations to determine which surgical approach will best suit your needs.
In conclusion, while there is no cure for lipedema, specific treatment strategies can help manage symptoms and enhance the day-to-day lives of those affected by this disorder. Incorporating a combination of compression therapy, manual lymphatic drainage, and considering surgical intervention when necessary might significantly improve the quality of life for people living with lipedema. Always seek consultation from a qualified healthcare professional when choosing the appropriate treatment plan for you.