How to Treat Dry Gangrene
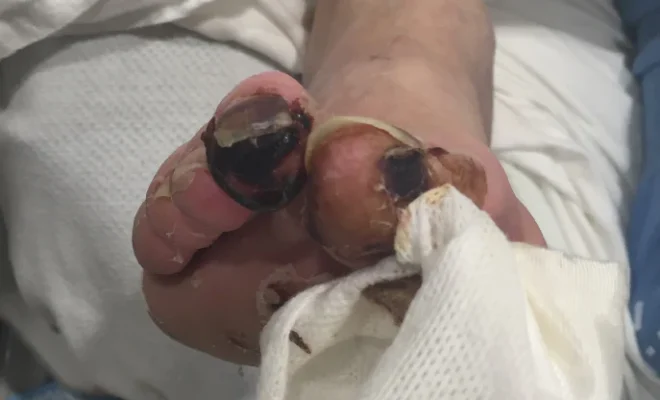
Introduction
Gangrene is a severe medical condition where body tissue dies due to loss of blood supply. It is typically caused by infection, injury, or an underlying disease. Dry gangrene is one of the types of this condition and occurs when there is a gradual decline in blood flow to a particular area, mostly affecting the extremities such as fingers and toes. Early detection and treatment of dry gangrene are crucial to prevent complications and save the affected body part. Here, we will explore how to recognize and treat dry gangrene effectively.
Symptoms of Dry Gangrene
It is essential to identify the signs and symptoms of dry gangrene to begin treatment immediately. Some common indicators include:
1. Discoloration – The affected area turns dark blue, brown, or black.
2. Dry or shriveled skin – The skin appears withered due to the loss of nutrients and oxygen.
3. Pain – Patients may experience mild to severe pain in the affected area, which may subside as nerve endings die out.
4. Cold temperature – The affected region might be significantly cooler than other parts of the body due to restricted blood flow.
Treatment Options for Dry Gangrene
1. Address underlying causes – Treatment should first focus on alleviating any diseases that cause poor blood circulation, such as diabetes or peripheral arterial disease (PAD). Proper management involves regular check-ups with healthcare providers, medications if necessary, and leading a healthy lifestyle.
2. Improve circulation – Ensuring adequate blood flow is vital to tissue healing. Methods can include physical therapy exercises, lifestyle changes (e.g., quitting smoking), or medications that help in dilating blood vessels and improving circulation.
3. Debridement – In some cases, doctors may need to remove the dead tissue surrounding the affected area through a process called debridement. This procedure helps prevent further tissue damage and infection.
4. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy – Patients can also benefit from hyperbaric oxygen therapy, which involves breathing 100% oxygen in a pressurized environment. This treatment aids in increasing the amount of oxygen in the blood, which helps heal the affected tissue and prevent infection.
5. Amputation – In severe cases where treatments fail to restore blood flow, amputation might be necessary to prevent the gangrene from spreading and save the patient’s life.
Prevention Tips
To reduce the risk of developing dry gangrene, it is essential to:
1. Manage chronic diseases – Ensure proper control of diabetes and peripheral arterial diseases with medications and regular check-ups.
2. Exercise regularly – Engage in physical activities to improve blood circulation and overall health.
3. Maintain good foot care – Routinely check your feet for any injuries or signs of infection; keep them clean and well-moisturized.
4. Quit smoking – Smoking constricts blood vessels, contributing to poor circulation; quitting can significantly reduce the risk of dry gangrene.
Conclusion
Dry gangrene is a severe medical condition that requires immediate attention as it may lead to serious complications if untreated. Early detection followed by appropriate treatments can help prevent its progression and save the affected body parts. Focus on addressing underlying health issues, maintaining proper circulation, and leading a healthy lifestyle to reduce your risk of developing dry gangrene. Reach out to your health care provider if you suspect any symptoms or need assistance managing your condition effectively.