How to Find Net Force: 9 Steps
Introduction:
Net force is the overall force resulting from the combination of individual forces acting on an object. The net force will determine the direction and magnitude of an object’s acceleration according to Newton’s Second Law of Motion. Learning how to find net force is a fundamental concept in physics, crucial for understanding various phenomena in everyday life. Here are nine simple steps to find the net force acting on an object.
Step 1: Identify All Forces Acting on the Object
First, understand what forces are acting on the object. Some common forces include gravity, friction, tension, and air resistance. Draw a vector arrow representing each force, pointing in the direction it acts.
Step 2: Determine the Magnitude of Each Force
Measure or calculate each force’s magnitude using tools or formulas specific to each type of force, such as weight equations for gravitational forces and friction equations for frictional forces.
Step 3: Break Down Diagonal Forces into Components
For any diagonal or inclined forces, break them down into horizontal and vertical components. Use trigonometric functions (sine and cosine) on your calculator with the angle value provided to determine these components.
Step 4: Organize Forces by Direction
List all positive (right/upward) and negative (left/downward) horizontal forces separately, followed by positive (upwards) and negative (downwards) vertical forces.
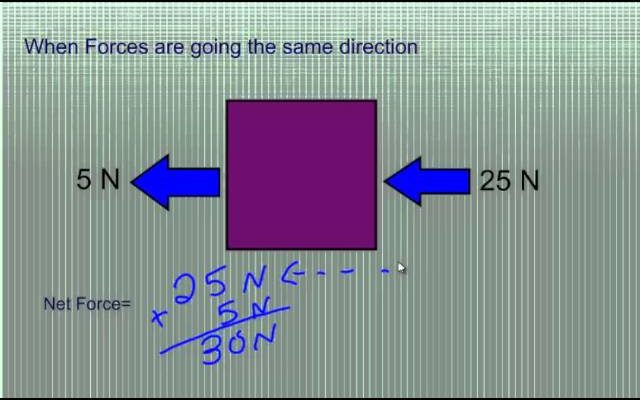
Step 5: Add Forces Acting in the Same Direction
Add up all positive horizontal forces and all negative horizontal forces separately. Do the same with vertical forces. This will result in a sum for each direction.
Step 6: Subtract Opposing Forces
Subtract the sum of negative horizontal forces from positive horizontal forces to obtain a single horizontal net force value. Repeat this for vertical forces.
Step 7: Square the Horizontal and Vertical Net Force Values
Square both the resulting horizontal net force value and vertical net force value.
Step 8: Add the Squares of Horizontal and Vertical Forces
Add these two squared values together to get a single number.
Step 9: Find the Square Root of the Resulting Value
Finally, find the square root of this number to determine the magnitude of the net force acting on the object. The direction of net force can be calculated using trigonometric inverse functions, such as arctan, by dividing the vertical net force value by the horizontal net force value.
Conclusion:
Finding net force is crucial for solving numerous physics problems involving motion, gravity, friction, and other physical forces. By following these nine simple steps, identifying and calculating net force should now be an easy task.

