How to calculate mortgage insurance
Introduction
Mortgage insurance is a financial tool that protects lenders from losses should a borrower default on their mortgage loan. It is typically required by lenders when borrowers make a down payment of less than 20% of the property’s purchase price. In this article, we will discuss the different types of mortgage insurance and how to calculate your mortgage insurance premium (MIP).
Types of Mortgage Insurance
There are two main types of mortgage insurance: Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI) and government-backed mortgage insurance. PMI is offered by private companies, whereas government-backed insurance can be obtained through specific government programs such as the Federal Housing Administration (FHA) and the Department of Agriculture (USDA).
1. Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI): PMI is typically required for conventional loans with a down payment of less than 20%. PMI rates vary depending on the percentage of your down payment, loan term, and credit score.
2. Government-Backed Mortgage Insurance: These include FHA, USDA, and VA loans. Each program has different requirements and eligibility criteria. The premiums for these programs vary based on loan type and down payment amount.
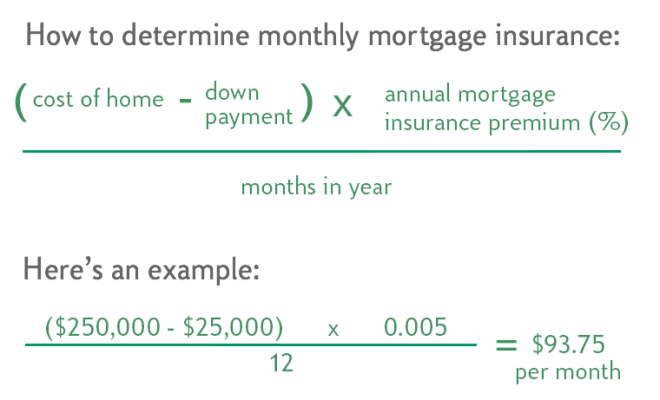
Calculating Your Mortgage Insurance Premium
Mortgage insurance calculations can vary based on the type of insurance you opt for. Below is a step-by-step guide highlighting the most common methods to calculate the MIP.
For Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI):
1. Determine Loan-to-Value (LTV): Divide your loan amount by the property’s appraised value or purchase price, whichever is lower. This will give you your LTV ratio.
2. Look Up PMI Rates: PMI rates often differ based on your LTV ratio and credit score bracket. You can obtain these rates from your lender or an independent PMI provider.
3. Calculate Annual Premium: Using the obtained PMI rate, multiply it with your loan amount. For example, if your PMI rate is 0.5% and your loan amount is $200,000, your annual premium would be $1,000 ($200,000 x 0.005).
4. Calculate Monthly Premium: Divide the annual premium by 12 to determine the monthly premium. In our example, the monthly premium would be $83.33 ($1,000 / 12).
For FHA Loans:
1. Determine Base Loan Amount: Deduct your down payment from the property’s appraised value or purchase price to get the base loan amount.
2. Calculate Upfront MIP: FHA charges an upfront MIP of 1.75% of the base loan amount. Multiply your base loan amount by 0.0175 to get your upfront MIP.
3. Calculate Annual MIP: Depending on your loan term and LTV ratio, FHA has different annual MIP rates, which can be obtained from the FHA website or lender. Multiply these rates by your base loan amount.
4. Calculate Monthly Premium: Divide the annual MIP amount by 12 to obtain the monthly premium cost.
In Conclusion
Understanding how to calculate your mortgage insurance premium is crucial to accurately estimate and plan for your monthly mortgage expenses. Factors such as loan type, down payment size, and credit score can impact the specific rate charged for mortgage insurance premiums, so it is advised to consult with a trusted lender in determining precise amounts tailored to your unique circumstances.






