How to calculate dollar cost average
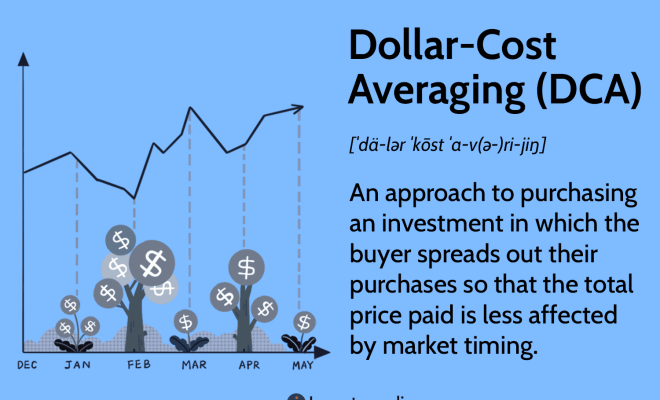
Dollar-cost averaging (DCA) is a popular investment strategy that involves spreading your investments over regular intervals, typically monthly. By investing the same amount consistently, you can reduce the impact of market volatility on your portfolio. This method effectively lowers your average costs per share over time by purchasing more shares when prices are low and fewer shares when prices are high.
In this article, we’ll discuss the benefits of dollar-cost averaging and provide you with a step-by-step guide on how to calculate it for your investments.
Benefits of Dollar-Cost Averaging
1. Reduces risk: Dollar-cost averaging minimizes the impact of short-term price fluctuations by spreading your investments over time. As a result, you can reduce your exposure to market timing risks and achieve a more predictable return on investment.
2. Encourages discipline: DCA instills discipline in investors by forcing them to invest regularly, regardless of market conditions. This consistency promotes long-term investing habits and helps avoid emotional decision-making.
3. Simplifies investing: With DCA, you don’t need to constantly monitor the markets or make multiple buy and sell decisions. All that’s required is a consistent investment plan at regular intervals.
Calculating Dollar-Cost Averaging
Step 1: Determine your investment budget
Decide how much money you want to invest each month and for what duration. This amount will remain the same throughout the investment period, ensuring consistency in your DCA strategy.
Step 2: Choose an investment
Select an investment vehicle such as stocks, mutual funds, or ETFs to apply the dollar-cost averaging strategy to. It’s essential to research and evaluate potential investments before committing to DCA.
Step 3: Set up an investment schedule
Determine a specific day each month for investing your fixed sum. Most investors choose to invest at the beginning or end of the month. However, you can select any day that works for your schedule.
Step 4: Calculate the number of shares to purchase
Divide your fixed investment amount by the current share price of your chosen investment. This will determine how many shares to buy for that month.
For example, if you are investing $500 and the share price is $50, you would purchase 10 shares ($500/$50 = 10).
Step 5: Repeat the process
Continue investing the same amount each month and calculate how many shares to purchase based on the current share price. Over time, you’ll accumulate more shares at lower prices and fewer shares at higher prices.
Step 6: Track your average cost per share
To calculate your dollar-cost average, divide the total amount invested across all intervals by the total number of shares purchased during those intervals.
For example, let’s say you invested $500 a month for three months:
– Month 1: Bought 10 shares at $50 each
– Month 2: Bought 12 shares at $41.67 each
– Month 3: Bought 8 shares at $62.50 each
Your total investment is $1,500 ($500/month * 3 months) and you’ve purchased a total of 30 shares (10+12+8). Your dollar-cost average is $1,500 / 30 = $50.
Conclusion
Dollar-cost averaging is a simple yet effective investment strategy that can help investors minimize risks and maintain discipline in their investments. By calculating and maintaining a consistent DCA plan, you can steadily build your portfolio over time without having to worry about timing the market perfectly.