3 Ways to Know if You Have a Hiatal Hernia
Introduction:
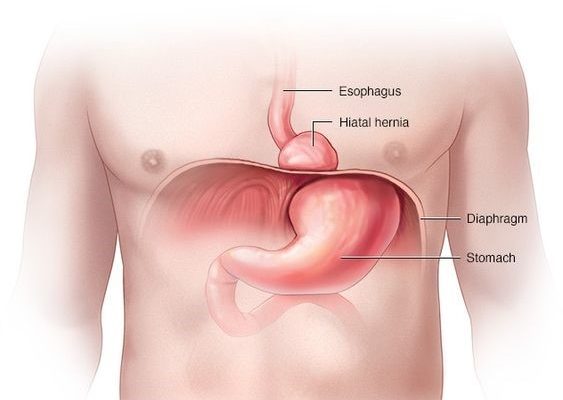
A hiatal hernia occurs when a part of your stomach pushes through the diaphragm and into the chest cavity. This condition can often be asymptomatic, but it may cause symptoms such as heartburn, acid reflux, and difficult swallowing. Knowing whether you have a hiatal hernia is crucial since it allows you to get proper treatment and prevent complications. Here are three ways to help you identify if you have a hiatal hernia.
1. Recognizing Common Symptoms:
The first step in identifying a potential hiatal hernia is recognizing its common symptoms. It’s essential to note that some people with hiatal hernias may not even experience any symptoms. However, some common symptoms could signify this medical issue:
– Heartburn: A burning sensation felt behind the breastbone that can worsen after eating or when lying down.
– Acid reflux: Regurgitation of stomach acid into the esophagus resulting in an uncomfortable sour taste in your mouth.
– Difficulty swallowing: Feeling like food is getting stuck in your throat or chest.
– Chest pain: Pressure or pain that can sometimes be mistaken for a heart attack.
– Shortness of breath: Trouble breathing, particularly when lying down or bending over.
2. Self-Assessment for Risk Factors:
Individuals with certain lifestyle factors and medical history are at increased risk for developing hiatal hernias. Assess yourself for these risk factors to gauge whether you might have this condition:
– Age: The likelihood of having a hiatal hernia increases with age, especially over 50.
– Obesity: Carrying excess body weight can put added pressure on your diaphragm, increasing the risk of a hiatal hernia.
– Smoking: Smoking weakens your diaphragm muscles and other connective tissues, contributing to the development of hiatal hernias.
– Previous surgery: A history of abdominal or chest surgery increases the risk of developing a hiatal hernia.
3. Seeking Medical Advice and Diagnostic Tests:
If you suspect that you might have a hiatal hernia based on your symptoms and risk factors, it’s vital to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis. Your doctor will ask about your medical history, perform a physical examination, and may suggest additional diagnostic tests to confirm the presence of a hiatal hernia:
– Endoscopy: A procedure that uses a flexible tube with a camera to view the esophagus, stomach, and surrounding areas.
– Barium swallow: An X-ray imaging technique that uses a special liquid called barium to visualize your digestive tract.
– Esophageal manometry: A test that measures the muscle contractions within the esophagus.
Conclusion:
Being aware of the common symptoms, evaluating your risk factors, and seeking medical advice are three crucial steps in identifying whether you have a hiatal hernia. Early detection and proper treatment can help alleviate your symptoms and prevent complications. If you suspect that you might have this condition, consult with your healthcare provider for guidance on diagnosis and treatment options.






